M6- Technical SEO
What you will learn: What technical SEO is (don’t be scared- I will keep this really simple), key technical factors that impact your site’s SEO and how to implement or fix them. This module will focus on actions, rather than learning lots of technical language.
Tasks (8): You will install a security certificate (if you don’t already have one), register your site with Google Search Console, check to see if your site is mobile friendly, install a caching plugin and speed up your site’s loading speed, run the Yoast configuration wizard, verify you have a site map and configure your social media settings in Yoast, create a Robots.txt file and run an SEO site audit.
Tools: Google Search Console, Really Simple SSL and SEOptimer
Read Time: 35 minutes
Task Time: Varies. Most of these tasks don’t take more than 10 minutes. However, registering your site with Google Search Console can take a couple of days while you wait for DNS propagation (more on this below so don’t worry if you don’t understand what this means), but the actual task time is only about 10 minutes.
What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to improving the technical aspects of a website in order to increase the ranking of its pages in search engines. We are going to keep this very simple and focus on the most important aspects. The good news is that WordPress and Yoast will do most of the work for us. However, there are a few things we need to do manually, so let’s get started!
Install a security certificate and redirect existing links
What is a security certificate?
It’s a digital file containing information that’s issued by a trusted third party (called a Certificate Authority) that indicates that the website is secured using an encrypted connection. They are often referred to as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Certificates because that is the technology they use to check that the site is secure.
There are different kinds of security certificates. Some are more secure than others.
Most sites have security certificates now but if yours doesn’t, you need to get one.
What are the benefits of having a security certificate?
‣ They will boost your SEO.
‣ Some browsers will put up a very scary warning that your site is insecure if you don’t have an SSL certificate or if yours has expired.
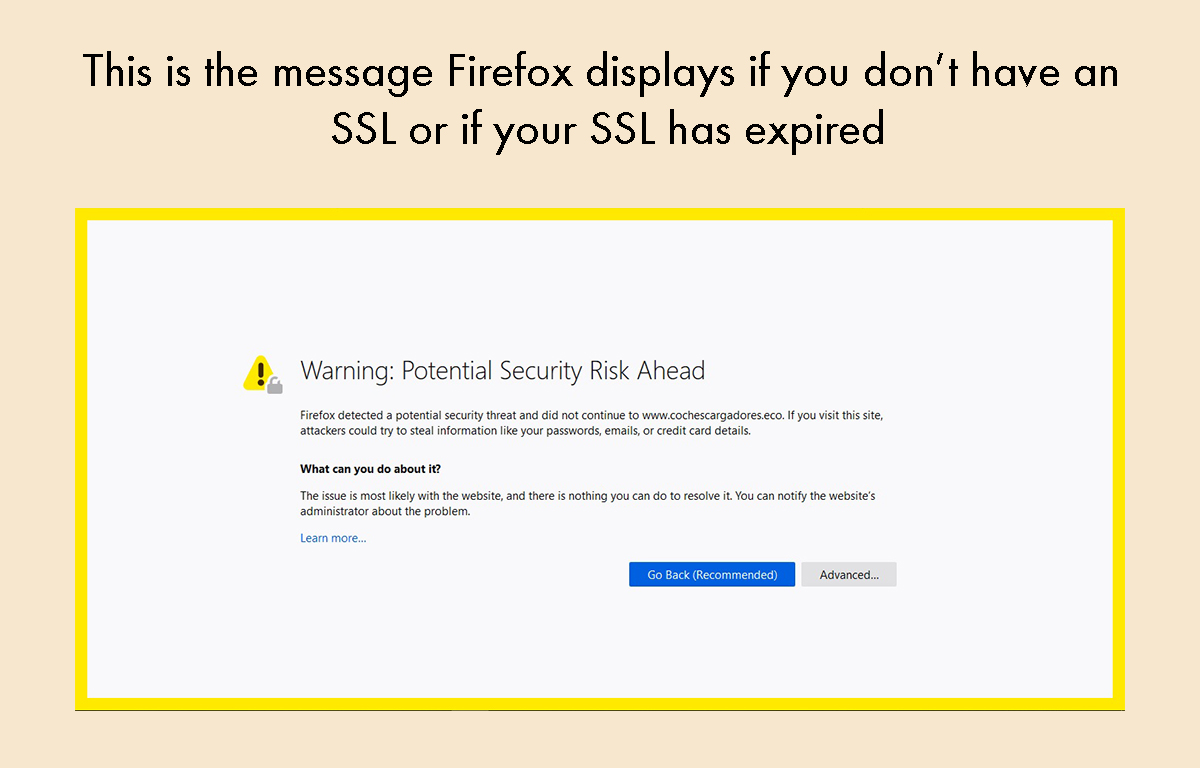
‣ They give your website visitors confidence that they are connected to your website, not a hacker-run fake. Many people worry about their sites getting hacked. The truth is it doesn’t happen very often but if it does, it can cost you a lot of money to fix it.
‣ They prevent people from intercepting data that is sent to your website. The most important example of this is credit card information and personal details that could lead to identify theft.
Do I need a security certificate?
Yes. However, unless you accept credit card information, bank details or other personal information (in excess of people’s names and email addresses), I personally think you can go for the free option if your hosting company provides one.
If you need a more secure option, I recommend you read this article and inform yourself before calling your hosting company: Choosing an SSL certificate
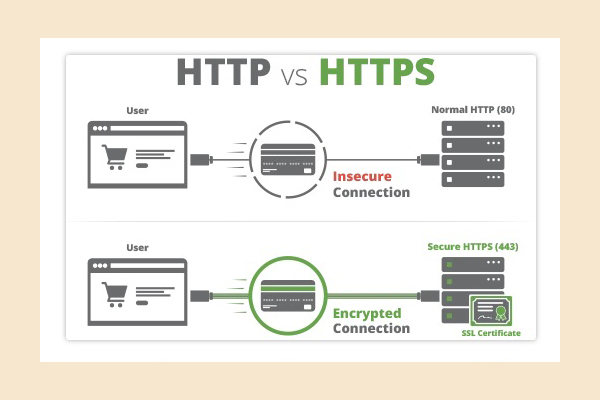
How do I know if I have a security certificate installed?
Look at your website’s url. If it has a security certificate, it will start with https. If it doesn’t have a security certificate, it will start with http. Example:
‣ No security certificate: http://bespoke-digital-solutions.com
‣ Security certificate: https://bespoke-digital-solutions.com
How do I get a security certificate?
You have to talk to your hosting company. Many hosting companies now provide basic security certificates for free. HostGator and Bluehost now provide free basic security certificates. GoDaddy and Media Temple still charge $75 per year for SSL certificates.
If you accept credit card or other payment details, or collect a lot of personal data from users, I highly recommend upgrading your security certificate if you are using a free one.
Configure your website to run over https
Tool: Really Simple SSL
You install this the same way you installed Yoast in Module 4. Here is how to do it:
- Hover your cursor over “Plugins,” which appears on the left sidebar in your WordPress dashboard.
- Type Really Simple SSL in the search bar that appears (reference the Yoast video if you can’t find it).
- Activate the plugin.
- You will see a notice asking you to enable SSL. Click it.
- Log in again.
- That’s it! The plugin will even redirect any of your backlinks.
Submit your website to Google Search Console
To do this, you will need to have your login credentials for your domain registrar at hand. Most likely, that is GoDaddy, Name.com or 1&1. You can always call your hosting company if you need help, or use one of your free vouchers and I will help you. If you have used your vouchers, you can always purchase additional consulting time from me. But call your host first if you get stuck- most decent hosting companies will walk you through the process.
Video: How to register you site with Google Search Console
Video: How to register your site with Google Search Console, Part 2
Ensure your site is mobile friendly
In 2018, Google included how mobile friendly sites are in their ranking system. They look at things such as how fast they load, how easy they are to read and if all the content loads properly on mobile. You can use their special tool to check how mobile friendly your site is. Just enter your site’s url and it will evaluate your site:
Tool: Google Mobile Friendly Test
If your site passes, you will see something that looks like this:
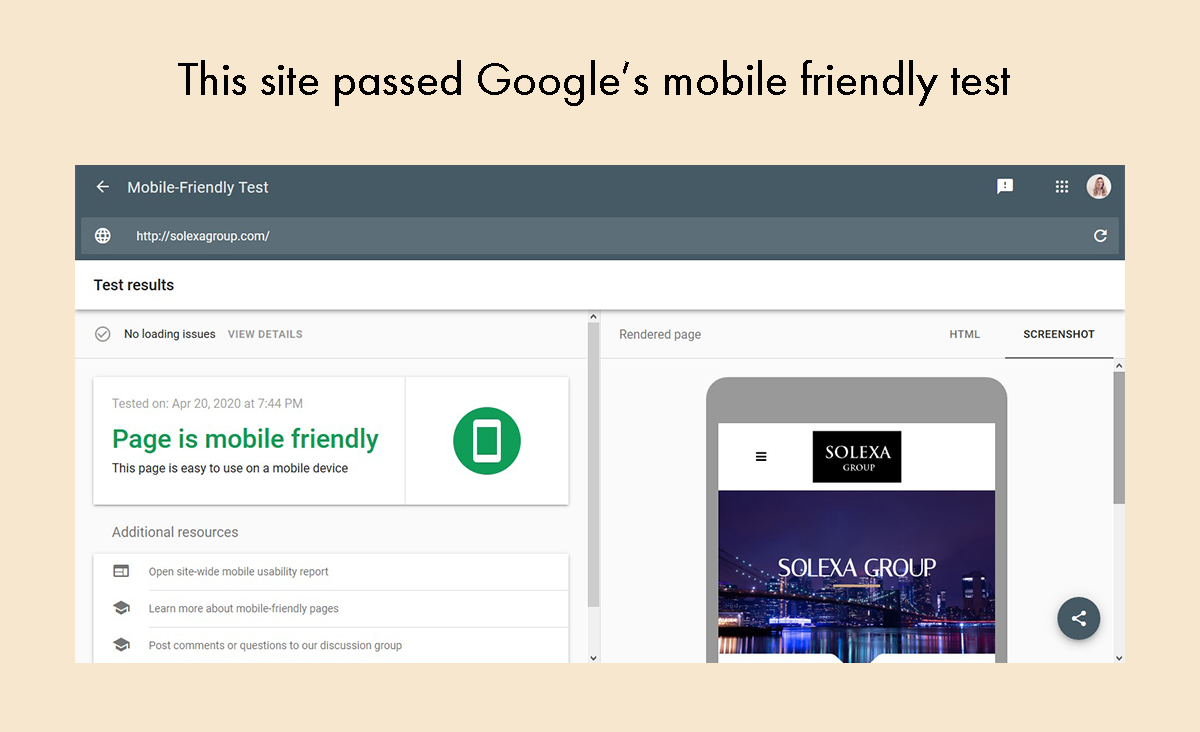
If it doesn’t pass, the tool will tell you what you need to fix. You may need to speak with your website developer about certain issues.
How to make your site load faster
A site needs to load quickly for good SEO. Google’s algorithms use page speed as a ranking factor.

You need a quickly loading site for reasons beyond SEO. If your site doesn’t load quickly, people are likely to bounce. Studies show that if a website takes more than three seconds to load, 40% of your visitors will bounce.
To demonstrate how important it is for a website to load quickly, back in 2012 Amazon did a study that estimated they would lose $1.6 billion in sales if their website loaded one second slower. If that is adjusted for 2019 (Amazon’s revenue has increased 1.43 times since 2012), that means they would lose $2.29 billion in sales if their website loaded one second slower.
Clearly, you want your site to load as quickly as possible! Following is a list of things you can do to make your site load faster.
Minimize image sizes
Your images should not be too high resolution. I typically make them no wider or taller than 1200 pixels, unless I am working with a photographer. Even then, I don’t make them any larger than 2800 pixels wide or tall. The bigger they are, the slower they load. Most hosts limit your image sizes for precisely this reason.
Although there are plugins you can use to minimize image size, I have had mixed results and can’t personally recommend any. I use Photoshop and minimize my image sizes in that application.
Clean up heavy code
Some website developers, particularly those that are very good at coding but don’t have much experience in WordPress, use code instead of bothering to learn WordPress. I have seen this slow loading speed down considerably.
Older WordPress templates can also be very code heavy and cause sites to load slowly.
If this happens, you will need to get someone to clean up the code. Alternatively, you might want to consider switching to a new WordPress template and finding a developer that has advanced WordPress skills to customize it.
The last task of this module teaches you to run an SEO audit. One of the things the audit checks for is the amount of code on the site, relative to images and other items. If your site is loading slowly and is code heavy, you need to speak with a developer. If your site is loading quickly but looks code heavy, it just means you have a relative small amount of images.
Install a caching plugin
Caching plugins help WordPress work more efficiently. They create a static version of your content. This removes many of the steps that take place when a web page is generated dynamically, as happens without a caching plugin.
There are a number of free caching plugins. My favorite is W3 Total Cache. Here is how to install and configure it:
Video: How to install and Configure W3 Total Cache
Change hosts
There are many cheap web hosting options available. However, the quality is often not very good. If you are serious about your online business, I recommend investing in high quality hosting.
Here is how hosting works. Most hosting plans are shared hosting. This means that you share a hosting company’s server with a number of their other customers. A server has a finite capacity. This means that claims by GoDaddy, HostGator and other hosting companies, that you have unlimited storage capacity and unmetered bandwith, are flat out lies.
If you have a small online business without much traffic, and relatively small page sizes, shared hosting should be more than sufficient. However, you should go with a reputable hosting company. I have a small, boutique web hosting company where I host sites for my clients. My servers are leased from LiquidWeb, who I think has the highest quality hosting in the world. Siteground also has very good quality shared hosting plans.
If you have a large online business, big web pages (you can check the size of your pages in the last video in this module: How to run an SEO audit) and/or lots of traffic, I recommend you spend the extra money to get a dedicated virtual private server. LiquidWeb offers them for as little as $99 per month and their excellent customer service team will help you set it up and manage it.
To learn more about web hosting, I refer you to this article: Web hosting for small businesses: What you need to know
Run Yoast configuration wizard
Now that you have your on-page SEO completed and are set up on Google Search Console, you are ready to run the Yoast configuration wizard. In this video I walk you through the process:
Video: How to run the Yoast Configuration Wizard
Create a site map and robots.txt file
Your website should always have a site map and a robots.txt file.
Site maps
A well constructed linking strategy ensures all your web pages are linked to each other, which helps Google crawl every page. We will learn how to do this in our next course: Level up your SEO. But even the best SEO person can forget a page, especially in large sites. Moreover, it can take time to develop enough content to link all of your pages. This is why you should submit a site map to Google. A sitemap lists a website’s important pages, making sure Google’s crawlers can find and crawl all of them. It also helps Google understand your website structure.
The good news is that Yoast automatically does this for you. Following is how to verify Yoast has created it. You can also check if your site has a site map when you do your SEO audit at the end of this course. The video below also walks you through some of Yoast’s settings.
Video: How to verify Yoast has created a site map
Robots.txt files
A robots.txt file is a file that tells web robots (also known as crawlers) which pages on your site to crawl. It also tells web robots which pages not to crawl.
Here is how to create a robots.txt file in Yoast:
Note: Some WordPress themes (the popular Divi is an example) override the option which lets you edit theme files. If this is the case, you will not see the “File Editor” option in Yoast. If this situation you have two options:
- If you know how to use FTP, create a robots.txt file in the root of your site.
- Call your web host and ask them to create one for you.
Regardless which of the above options you chose, I recommend putting the following code in your file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.ph-
Run an SEO audit
This is your final step of this course! You are going to check your work and see if there is anything you missed or anything you need to address. To do this, run an SEO site audit. I will walk you through the process in the following video. Below that is a checklist of things you should look for.
Tool: Seoptimer
Video: How to run an SEO site audit
If you have successfully completed all the tasks in this course, your site should fare well in the SEO audit. Here are some additional things to look for in your SEO audit:
- Make sure you have enough content. If you don’t, Google can’t crawl your site effectively. Consider taking the next course, Level up your SEO, to learn how to develop a consistent blogging strategy that effectively uses cornerstone content to create content and link it together properly.
- Broken links. One or two is not a disaster, but you should fix them. I teach you how to do this in the next course. If you have a lot of broken links, you should get them fixed promptly.
- Check the indexing portion carefully. If your site fails any of these tests, you need to speak to your developer or contact Mary Clare.
- Make sure your site isn’t running Flash player. Flash player has many bugs and drains the memory and battery of mobile sites. Steve Jobs deemed is so bad that it won’t run on any Apple product. If you have Flash player on your site, I strongly suggest you find a replacement.
- An iFrame (Inline Frame) is an HTML document embedded inside another HTML document on a website. They are often used to insert content from other sources into web pages (for example, YouTube videos). Ten years ago, hackers used iFrames to attack a couple high profile sites. Security has improved much in recent years. The SEO issue is that iFrames can sometimes prohibit Google from indexing a web page. Personally, I would never use an iFrame if any kind of secure data is involved. However, I am never had a problem inserting YouTube videos in web pages. If you want to be very cautious you should replace all iFrames (example: host your own videos). It’s your call!
- Check your site loading speed. If it is loading slowly, use the SEO audit to figure out why and rectify the problem.
- Make sure you have no JavaScript errors. If you have them, find a developer and get them to fix the problem.
- Fix any errors the audit identifies as High Priority. You shouldn’t have any if you have completed all the tasks in this course and your website is in good shape. You can always contact Mary Clare if you have an issue.
Takeaways
- Your website pages should now be effectively optimized for search.
- You have tools, Google Search Console, Yoast and Seoptimer, to monitor and improve your site’s SEO on an ongoing basis.
- You have completed the course: CONGRATULATIONS!!!!
Video: Congratulations, next steps and 10% off on next course
Want 10% off your next course? If you write a positive review of this course on my LinkedIn page, I will send you a coupon code for 10% off on your next course.
Mary Clare’s LinkedIn profile: Mary Clare Bland


